Blog
PRACTICAL CONCEPT OF ELECTROSATICS | ADHYAYAN IAS
- April 24, 2024
- Posted by: Sushil Pandey
- Category: Daily Blogs Free Resources IIT-JAM Study material
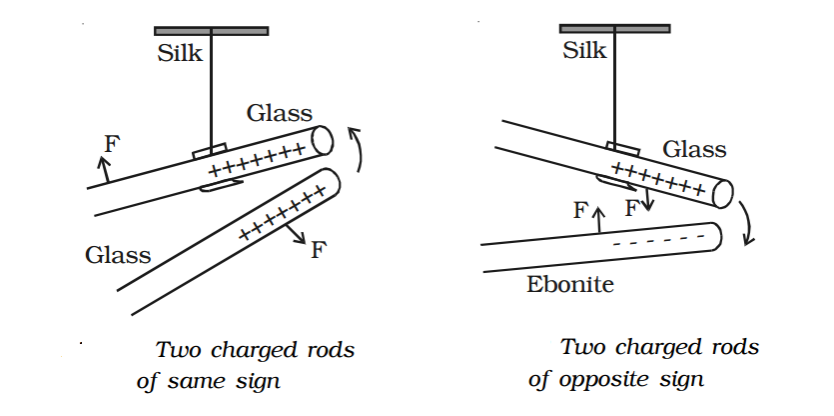
What Are Conductive vs. Insulative Materials?
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) happens from friction between conductive and less conductive or non-conductive materials.
Non-conductive, or insulative, materials have high surface resistivity, limiting electrons’ flow over and through the material. Static charges are difficult to ground and remain on the surface of these materials.
On the other hand, conductive materials have low resistance, so electrons move easily over and through the material. Charges go to the ground or transfer to a nearby conductive material.
People are the main cause of ESD because we introduce an insulative object, like a piece of clothing, into the conductive environment. When the stored, static charge on the surface comes into contact with a conductor like a part or device, ESD occurs.
What Is Static Dissipative?
A dissipative material has medium surface resistivity, meaning electricity flows through slower and with greater control than conductive material. Also known as static-dissipative or electro-dissipative material, dissipative material is best for ESD environments since it allows charges to flow slowly and in a controlled manner.
What Is Antistatic?
Anti static material prevents the buildup of static electricity and can be either conductive or dissipative. However, insulative materials are not antistatic – they stop the flow of electric charges, but they do not prevent static from accumulating.
